Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 2.3: Difference between revisions
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
'''polling''' Number of milliseconds between each data to be sent to the raspberrypi. | '''polling''' Number of milliseconds between each data to be sent to the raspberrypi. | ||
'''kcal''' Current or Volatge calibration coefficient. | '''kcal''' Current or Volatge calibration coefficient. Formerly Ical or Vcal. Must be 8 numbers long. | ||
'''vest''' Voltage to compute estimated power. Usually 240V or 110V. Must be present even is not used. Set vest=1 to obtain output as ampere instead of watts. Set vest=1000 to get milliampere. | '''vest''' Voltage to compute estimated power. Usually 240V or 110V. Must be present even is not used. Set vest=1 to obtain output as ampere instead of watts. Set vest=1000 to get milliampere. Only applies for channel type number 5 (estimated power). | ||
'''Nnode''' Number of combination node to compute. | '''Nnode''' Number of combination node to compute. | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 3 June 2017
Overview
RPICT board using Atmega microcontrollers can be configured over serial using a utility written in python. This involves boards RPICT7V1 RPICT4V3 version 2 and RPICT8.
Current version allows changes of
- Output format (csv or Emoncms)
- Nodeid (emoncms only)
- Polling (polling interval of data)
- Ical (current calibration value)
- Vcal (Voltage calibration value)
- Vest (estimated voltage for power estimate)
RPICT Configuration tool
The configuration tool can be downloaded directly from the raspberrypi:
$ wget lechacal.com/RPICT/lcl-rpict-config.py.zip $ unzip lcl-rpict-config.py.zip
Reading current configuration
Using the configurator without option only read the configuration stored in the board.
$ ./lcl-rpict-config.py
This yields
# RPICT Configuration Utility # Read only # Now reset RPICT hardware
Once the board has received the reset the configuration will be shown. How to reset the board
# # Configuration in memory: # # Structure: 0xa0 # Format: 0 # NodeId: 11 # Polling: 5000 # ICAL: 83.330002 # VCAL: 560.000000 # VEST: 240.000000 #
Note. Every time the configuration is read from the board it stores a config file in /tmp/rpict.config.
Modify the configuration
To change the values the configurator must be fed with a file containing the new values. We will use the example of a RPICT7V1. Such file looks as below.
[main] format = 0 nodeid = 11 polling = 5000 kcal = 545.0 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 vest = 0 Nnode = 7 Nchan = 15 HWSCT = 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 HWMCPSCT = 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 HWVOL = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 HWMCPVOL = 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 CHTYPE = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 CHID = 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255
We save this file in rpict7v1.conf. Then we can now start the configurator with the -w option.
$ ./lcl-rpict-config.py -w rpict7v1.conf
Once reset the configurator will read the old config then write the new config and display the newly stored one again.
# RPICT Configuration Utility # Configuration will be overwritten (Ctrl C to cancel) # Now reset RPICT hardware # # Configuration in memory: # # Structure: 0xa0 # Format: 0 # NodeId: 10 # Polling: 5000 # ICAL: 83.330002 # VCAL: 545.000000 # VEST: 240.000000 # # Writing configuration with file rpict3t1.conf # # Configuration in memory: # # Structure: 0xa0 # Format: 1 # NodeId: 11 # Polling: 5000 # ICAL: 83.330002 # VCAL: 560.000000 # VEST: 240.000000 #
The configuration file
The configuration file fed into the utlity must have the format below:
[main] format = 0 nodeid = 11 polling = 5000 kcal = 545.0 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 83.33 vest = 0 Nnode = 7 Nchan = 15 HWSCT = 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 HWMCPSCT = 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 HWVOL = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 HWMCPVOL = 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 CHTYPE = 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 3 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 CHID = 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255 255
format indicate which format output will be used. Must be an integer number.
0 - CSV
1 - Emoncms
2 - Emoncms as float (must have datatype f setup in emonhub config)
nodeid Only used in emoncms format. Will set the node id.
polling Number of milliseconds between each data to be sent to the raspberrypi.
kcal Current or Volatge calibration coefficient. Formerly Ical or Vcal. Must be 8 numbers long.
vest Voltage to compute estimated power. Usually 240V or 110V. Must be present even is not used. Set vest=1 to obtain output as ampere instead of watts. Set vest=1000 to get milliampere. Only applies for channel type number 5 (estimated power).
Nnode Number of combination node to compute.
Nchan Number of channels (or fields) to output.
HWSCT Pin configuration of a current input.
HWMCPSCT Master or slave identifier for current input.
HWVOL Pin configuration of a voltage input.
HWMCPVOL Master or slave identifier for voltage input.
Combination nodes
Combination nodes are small programs in the microcontroller that computes power given a current/voltage couple.
Four given parameters must be provided. They are the pin numbers where to find the current and voltage and also which slave (or master) is to be used.
For example if
HWSCT = 8 HWMCPSCT = 6 HWVOL = 1 HWMCPVOL = 10
will use current ct1 (8) on slave 1 (6) computed against voltage1 (1) on master board (10).
The tables below gives all pin assignment:
| Pin number | RPICT7V1 | RPICT8 | RPICT4V3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | V1 | CT8 | V3 |
| 2 | CT7 | CT7 | V2 |
| 3 | CT6 | CT6 | V1 |
| 4 | CT5 | CT5 | nc |
| 5 | CT4 | CT4 | CT4 |
| 6 | CT3 | CT3 | CT3 |
| 7 | CT2 | CT2 | CT2 |
| 8 | CT1 | CT1 | CT1 |
| Pin number | Board type |
|---|---|
| 10 | Master |
| 6 | Slave 1 |
| 7 | Slave 2 |
| 8 | Slave 3 |
| 9 | Slave 4 |
Channels
We are refering as a channel here a data stream to be sent out. For example Vrms and Realpower derived from a same sensor will be two different channels.
These are configured with two numbers. The first one is the combination id defined above. Note the first combination id is zero (0). The second number identifies the type of channel. For example:
CHTYPE = 3 CHID = 0
Uses voltage/current combination node id 0. Channel type 3 which is Vrms (as the table below describes).
The table below shows the convention being used:
| code | Channel Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | |
| 1 | Real Power | Real Power in Watts |
| 2 | Apparent Power | Apparent Power in Watts. This is Irms*Vrms |
| 3 | Vrms | Rms Voltage in Volts |
| 4 | Irms | Rms current in milliAmps |
| 5 | Estimated Power | Estimated Power in Watts. This is Irms*Vest. |
How to reset the board
Use a small jumper to link the reset pin with the ground. This can be found on the 3x2 6 pin ISP connector.
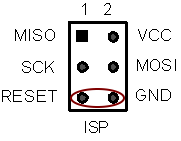
Make contact with the two pins then remove the jumper. This will reset the board.