Current Transformer Conditioner: Difference between revisions
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
G = Vadc/Vct/2√2 | G = Vadc/Vct/2√2 | ||
''Vadc'' | ''Vadc'' is the full scale voltage value of the ADC. Usually 5V or 3.3V.<br> | ||
''Vct'' | ''Vct'' is the output voltage of the current transformer at maximum desired value (rms). | ||
===Example=== | ===Example=== | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 29 March 2019

The CT Conditioner allows to connect a Current Transformer to an Arduino Analog pin.
- Supports both current and voltage output CT.
- 3.5mm Jack connector CT port.
- Amplification easily setup by mean of a resistor.
- Zero offset can be set to Vcc/2 onboard. Or use an external reference.
- Uses instrument amplifier AD623 for accurate result.
- Provision of a burden resistor mounting for current output CTs.
- Minimum setup uses 3 wires. +5V Gnd and analog out.
- Dimensions: 24x24mm
Usage

Connect the CT sensor to the jack connector. Then connect 3 wires to the Arduino. The 3 wires to connect are
CT conditioner -> Arduino Vcc -> 5V Gnd -> Gnd Out -> A0
Note Vcc can also be connected to 3.3V.
Compatible CT
Any CT with a 3.5mm jack connector will be supported.
Voltage CT
No burden resistor should be fitted using a Voltage CT. These are commonly
SCT-013-005
SCT-013-010
SCT-013-015
SCT-013-020
SCT-013-025
SCT-013-030
SCT-013-050
SCT-013-060
Current CT
A burden resistor must be used when using current output CT. These are commonly
SCT-013-000
SCT-006
SCT-019
Sketch Example
A simple arduino sketch can be used to read the value every seconds. See the example below.
// CT Conditioner Demo // Version 1.0 // lechacal.com // // Required Libraries // RPICTlib 1.0.0 // http://lechacal.com/RPICT/RPICTlib/RPICTlib_v1.1.0.zip // // Always Include these 4 lines at the top of the sketch #include "RPICTlib.h" // Include the library uint8_t ADC_BITS = 10; // Some mandatory global setup uint16_t ADC_COUNTS (1 << ADC_BITS); uint16_t ADC_REF = 5000; int sInterval = 400; // 400usec is 2.5kHz sampling interval (internal sampling) int NUMBER_OF_SAMPLES = 1000; // We will use 1000 samples to measure the rms signal. CurrentNode ct1; // Our CT we will compute with void setup() { Serial.begin(38400); // Open the serial port ct1.init(A0, 30.0); // Analog port A0, 30 scaling factor (using a SCT-013-030) } void loop() { ct1.calcIrms(NUMBER_OF_SAMPLES, sInterval); // Measure and compute Irms Serial.println(ct1.Irms); // Print the result delay(1000); // wait 1 second }
Default Setup
By default the CT conditioner comes with no resistors fitted for both Burden and Gain.
This means this is ready for a voltage output CT and the Gain is 1.
Resistor
Fitting
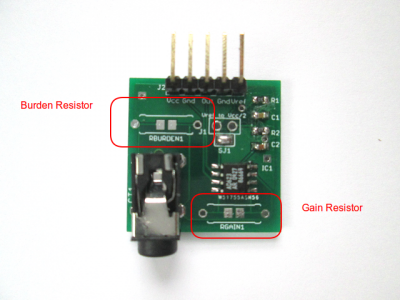
There 2 types of resistor the user can fit on the CT conditioner. These are not mandatory but will help optimising the measurement.
Both surface mount and though hole resistor are supported. Surface mount resistor case are 0805 size.
Burden Resistor
When a current output CT sensor is used a resistor must be soldered to the CT conditioner. It it usually recommended to use a low value resistor. ALso the datasheet of the CT should have some indication on the maximum resistor to use. Burden resistor is also called sampling resistor in some documentations.
Note that you do not need a burden resistor if the CT is voltage output.
Amplification
A second resistor can be fitted on the CT conditioner to adjust the amplification level. Amplification can be required if it is found the levels are too low. For low currents this can increase resolution.
From a desired gain the resistor can be calculated as follow
Rg = 100000/(G -1)
G is the Amplification Gain.
Rg is the resistor value in ohm.
The formulae below should be used to estimate the Gain.
G = Vadc/Vct/2√2
Vadc is the full scale voltage value of the ADC. Usually 5V or 3.3V.
Vct is the output voltage of the current transformer at maximum desired value (rms).
Example
Here is an example of Gain calculation.
Let's take the SCT-013-030. This outputs 1V at 30A (both rms and peak). Hence ICAL = 30.
Using an Arduino UNO the ADC has 5V reference by default. Hence Vadc = 5.
We would like to measure 30A (i.e. 1V) at the maximum scale of the ADC. Hence Vct = 1.
We can estimate the required gain as follow:
- G = 5/1/2√2 = 1.77.
Then the required resistor for this Gain is:
- Rg = 100000/(1.77-1) = 130Kohm.
We can now calculate the theoretical scaling coefficient to enter in the sketch:
- newICAL = ICAL/G = 30/1.77 = 16.95
We will then fit a 130kOhm resistor and enter in the sketch
ct1.init(A0, 16.95);
Recommended Values
| CT | Output Type | Rburden | Rgain (for 5V) | ICAL (for 5V) | Rgain (for 3.3V) | ICAL (for 3.3V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCT-013-005 | Voltage | None | 130 kΩ | 2.83 | None* | 5.0 |
| SCT-013-010 | Voltage | None | 130 kΩ | 5.66 | None* | 10.0 |
| SCT-013-015 | Voltage | None | 130 kΩ | 8.49 | None* | 15.0 |
| SCT-013-020 | Voltage | None | 130 kΩ | 11.31 | None* | 20.0 |
| SCT-013-025 | Voltage | None | 130 kΩ | 14.14 | None* | 25.0 |
| SCT-013-030 | Voltage | None | 130 kΩ | 16.96 | None* | 30.0 |
| SCT-013-050 | Voltage | None | 130 kΩ | 28.28 | None* | 50.0 |
| SCT-013-060 | Voltage | None* | 130 kΩ | 33.94 | None* | 60.0 |
| SCT-006 | Current | 10 Ω | 17 kΩ | 11.62 | 28 kΩ | 17.5 |
| SCT-013-000 | Current | 10 Ω | 40 kΩ | 56.57 | 75 kΩ | 85.71 |
| SCT-019 | Current | 10 Ω | 24 kΩ | 116.13 | 40 kΩ | 171.43 |
* For all the None* calculated amplification is 1.17. Being close to 1 we do not consider it is worth installing a resistor.
Vref

Vref is the center of the waveform and is set on the Amplifier.
Why? As most ADC scale are set between 0 and 5V (or other positive voltage) is makes it difficult to measure a waveform with a negative part. We will miss the negative part due to the limit at 0. To face this we can offset the signal higher at say 2.5V. Then when negative the waveform will be below 2.5V and above when positive.
By default Vref is connected to Vcc/2 (2.5V or 1.65V). This is done with the solder blob shown on this picture. The Vcc/2 is achieved using a voltage divider with 2x 10k resistors on the board.
If you prefer using an external Vref then disconnect Vref from Vcc/2 by removing the blob with a soldering iron. Then Vref can be set from an external source on one of the pin of the CT conditioner.

