Raspberrypi Current and Temperature Sensor Adaptor: Difference between revisions
| Line 167: | Line 167: | ||
The above example is for the board with 2CT and 1 temperature sensor. See [[python example 3CT | here]] for the python example using the board with three CT sensors. | The above example is for the board with 2CT and 1 temperature sensor. See [[python example 3CT | here]] for the python example using the board with three CT sensors. | ||
===Using SPIOT=== | |||
Download and install SPIOT on a given server. This could be the raspberrypi itself. | |||
From the downloaded archive there is a directory called rpi containing python scripts and configuration file. Copy all these files on the raspberrypi (if not already there). | |||
Make sure all .py files are executable: | |||
$ chmod 755 *.py | |||
Open the spiot.config file and modify the csv_forward section. port and hostname variable will be the most important ones for a first test. Keep apikey and node as they are to follow this example. | |||
[csv_forward] | |||
port = /dev/ttyAMA0 | |||
hostname = myserver/spiot | |||
apikey = qbG31dQxFlG55mNM8G5ZTFkF0mrUbWg5 | |||
node = 20 | |||
baud = 38400 | |||
Then run the spiot_csv.py utility. | |||
$./spiot_csv.py | |||
Then point your webbrowser to the link below: | |||
http://myserver/spiot/realtime.html?apikey=qbG31dQxFlG55mNM8G5ZTFkF0mrUbWg5&node=20&fields=f001 | |||
The last 5 minutes of the first channel will be shown on a graph. | |||
===Using Emoncms=== | ===Using Emoncms=== | ||
Revision as of 20:07, 21 February 2017
RPICT Series
RPICT series are a set of Raspberrypi adaptor for current sensor (SCT) and temperature sensor. This page will introduce generalities concerning the RPICT series. Information for each individual board can be found below.
- RPICT2T1 - 2 CT 1 temperature.
- RPICT3 - 3 CT.
- RPICT3T1 - 3 CT 1 Temperature
- RPICT3V1 - 3 CT 1 AC Voltage
- RPICT4V3 - 4 CT 3 AC Voltage
- RPICT4T4 - 4 CT 4 Temperature
- RPICT7V1 - 7 CT 1 AC Voltage.
- RPICT7V1_v2.0 - 7 CT 1 AC Voltage.
- RPICT8 - 8 CT
- RPICT1 - deprecated
- RPICT1T1 - deprecated
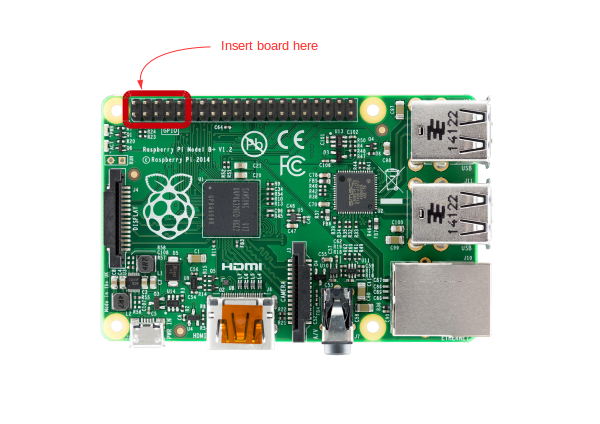
All RPICT board connect to the GPIO connector and provide data via serial interface. An Arduino programmable microcontroller (Attiny85 or ATtiny84) runs the board. Source code for the microcontroller is freely available and can be modified for adaptation.
There are several options for logging and viewing the data. Python or Emoncms or anything able to read a serial port.

Technical Specifications
Current Sensor

Recommended sensor: SCT-013-000 50mA/100A
Burden Resistor: 24 Ohm
Connector: 3.5mm Jack
Note this sensor only measures Alternative Currents (AC).
Measured range
The range is determined by the burden resistor.
The default range is 100A on all RPICT series which correspond to a burden resistor of 24 Ohm. The table below shows alternative ranges with their associated burden resistor values.
| Range (Rms Amps) |
Burden Resistor (Ohm) |
Calibration Coefficient (theoretical) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 24 | 83.33 |
| 60 | 39 | 51.28 |
| 50 | 47 | 42.55 |
| 30 | 75 | 26.67 |
| 25 | 91 | 21.98 |
| 20 | 120 | 16.67 |
| 15 | 160 | 12.5 |
| 10 | 240 | 8.333 |
| 5 | 470 | 4.255 |
Temperature Sensor
Connector: 3.5mm Jack
The intended temperature sensor is the DS18B20 which can be configured in either parasite or normal mode.
The connection to a 3.5mm jack connector is shown below.
NOTE: Raspberrypi must be switched off while connecting and disconnecting the temperature sensor.
Voltage Sensor
An AC/AC adaptor is used to measure Voltage. We have a set of recommended adaptors:
- UK: 77DB-06-09
- EU: 77DE-06-09
- US: 77DA-10-09 or CT3957-NA
View/Record data
Using plain Linux terminal
It is possible to read the data output directly from a linux terminal. i.e. reading the serial port.
Before hand you must ensure two things before getting this to work:
1/ The firmware of the board has been set to use output as CSV. Relevant sketch can be downloaded below. See OUTPUT_AS_CSV variable.
2/ The ttyAMA0 or ttyS0 serial on the raspberrypi is free. See this link here.
As an exmaple the output from the RPICT2T1 adaptor board will be in the format below. power in kw. temperature in deg celsius.
power1,power2,temperature
Then on the Raspberrypi you can issue the commands
$ stty -F /dev/ttyS0 raw speed 38400 $ cat /dev/ttyS0
The terminal should then show something like this below
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ cat /dev/ttyS0 46,52,19.46 47,52,19.46 45,54,19.46 47,56,19.46
On some older system you might have to use ttyAMA0 instead of ttyS0
Why do I see a different output?
Using Python basic script
Using the same sketch as mentioned above a python script can be used to work with the data. The example script below will be a good starting point.
First of all make sure you have python-serial package installed
$ sudo apt-get install python-serial
Then copy the following into an executable file and run it.
#!/usr/bin/python
import serial
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyS0', 38400, timeout=1)
try:
while 1:
response = ser.readline()
z = response.split(",")
if len(z)>=2:
print "Power 1: %s Watts" % z[0]
print "Power 2: %s Watts" % z[1]
print "Temperature: %s Degrees" % z[2][:-2]
except KeyboardInterrupt:
ser.close()
The above example is for the board with 2CT and 1 temperature sensor. See here for the python example using the board with three CT sensors.
Using SPIOT
Download and install SPIOT on a given server. This could be the raspberrypi itself.
From the downloaded archive there is a directory called rpi containing python scripts and configuration file. Copy all these files on the raspberrypi (if not already there).
Make sure all .py files are executable:
$ chmod 755 *.py
Open the spiot.config file and modify the csv_forward section. port and hostname variable will be the most important ones for a first test. Keep apikey and node as they are to follow this example.
[csv_forward] port = /dev/ttyAMA0 hostname = myserver/spiot apikey = qbG31dQxFlG55mNM8G5ZTFkF0mrUbWg5 node = 20 baud = 38400
Then run the spiot_csv.py utility.
$./spiot_csv.py
Then point your webbrowser to the link below:
http://myserver/spiot/realtime.html?apikey=qbG31dQxFlG55mNM8G5ZTFkF0mrUbWg5&node=20&fields=f001
The last 5 minutes of the first channel will be shown on a graph.
Using Emoncms
Emoncms is probably the most complete and user friendly interface.
To use it the RPICT board must output in the Emoncms specific format. Make sure you purchase the correct output or are able to reflash the firmware to modify it.(Note we will come soon with a CSV to Emoncms forwarder). You will have to set the raspberrypi image accordingly to what the Emoncms website suggest.
The Raspberripy OS distribution provided by OEM for the Raspberry emonbase must be used for this purpose. The default sketch will work for the use of EmonCMS. In the Node section of emoncms the device with ID 11 will appear on its own.
The Adaptor emulates a RFM12Bpi unit communication pattern. i.e. What will be sent to the Raspberrypi serial port will look as if it was sent by the RFM12Bpi.
The sketch is provided in the specific page of the RPICT type. In the sketch the OUTPUT_AS_CSV variable should be set to false to enable EMoncms output.
Flash the firmware
The onboard microcontroller can be re-programmed. This can to done to change output format from CSV to EMoncms or to change the Voltage for power calculation. This link is a tutorial to upload Arduino sketches to the Attiny85.
Files
Arduino Sketches
Remember to modify the OUTPUT_AS_CSV variable to choose between csv or emoncms output.
Note. Default Power calculation is based on a voltage of 240V.
Related Howto
Free up the ttyAMA0 serial port
How to program an Attiny85 or Attiny84