RPICT3V1: Difference between revisions
| (37 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:IMG_0473_small.png | 300px | right]] | ||
This page is for board specific information. More information can be found on the [[Raspberrypi_Current_and_Temperature_Sensor_Adaptor | generic page for RPICT series]]. | This page is for board specific information. More information can be found on the [[Raspberrypi_Current_and_Temperature_Sensor_Adaptor | generic page for RPICT series]]. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 7: | ||
* 1 AC Voltage sensor. | * 1 AC Voltage sensor. | ||
* Compute RealPower, ApparentPower, PowerFactor, Vrms, Irms. | * Compute RealPower, ApparentPower, PowerFactor, Vrms, Irms. | ||
* Fit on | * Fit on the 2 holes mounting pattern for Raspberrypi. | ||
* Arduino Attiny84 Microcontroller. | * Arduino Attiny84 Microcontroller. | ||
[[File:Link_to_the_shop.png | link=http://lechacalshop.com/en/rpict-series/20-raspberrypi-1x-current-sensor-adaptor-1-voltage-emoncms.html]] | |||
=Compatibility= | =Compatibility= | ||
[[File: | [[File:IMG_0586_mod.JPG | 300px | right]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| Line 25: | Line 22: | ||
|Raspberrypi 1 A | |Raspberrypi 1 A | ||
|Yes | |Yes | ||
|- | |||
|Raspberrypi 1 B | |||
|No mounting holes. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|Raspberrypi 1 B+ | |Raspberrypi 1 B+ | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Raspberrypi 4 B | |Raspberrypi 4 B | ||
|Yes | |||
|- | |||
|Raspberrypi 5 | |||
|Yes | |Yes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 49: | Line 52: | ||
The RPICT3V1 must have a voltage sensor to compute Real Power. If you do not want to use a voltage sensor and prefer measuring just current then the [[RPICT3T1]] might be more appropriate. | The RPICT3V1 must have a voltage sensor to compute Real Power. If you do not want to use a voltage sensor and prefer measuring just current then the [[RPICT3T1]] might be more appropriate. | ||
(Note it is possible to use a different sketch (firmware) to make the RPICT3V1 using estimated voltage. However you will have to flash the unit for that.) | (Note it is possible to use a different sketch (firmware) to make the RPICT3V1 using estimated voltage. However you will have to flash the unit with a special programmer for that.) | ||
==Recommended sensors== | ==Recommended sensors== | ||
[[File: | [[File:IMG_0587_mod.JPG | 300px | right]] | ||
* AC Current sensor: | * AC Current sensor: | ||
| Line 58: | Line 61: | ||
** SCT-019 | ** SCT-019 | ||
** SCT-006 | ** SCT-006 | ||
** SCT-024 400A/100mA | |||
** SCT-031 600A/100mA | |||
* AC Voltage sensor: | * AC Voltage sensor: | ||
** [[ZMPT101B_Module_1x_v2 | ZMPT101B Module]] | |||
** UK: 77DB-06-09 | ** UK: 77DB-06-09 | ||
** EU: 77DE-06-09 | ** EU: 77DE-06-09 | ||
| Line 69: | Line 75: | ||
See general instructions for configuration below: | See general instructions for configuration below: | ||
[[Attiny Over Serial Configuration | Configuration over serial for sketch version | [[Attiny Over Serial Configuration A2 | Configuration over serial for sketch version 2.0 & 2.1]]. | ||
Version 2.0 & 2.1 can be configured using the web tool. | |||
[ | [http://lechacal.com/RPICT/config/generator/rpict3v1_v1.0/ Online Config Generator] | ||
==Default Data Output== | |||
If you are running an old version of the firmware click on the link below related to your version. | |||
[[RPICT3V1 Sketch version 1.3 documentation]] | |||
Using the default sketch '''version 2.0''' and above the output is <br> | Using the default sketch '''version 2.0''' and above the output is <br> | ||
| Line 90: | Line 91: | ||
* RealPower in Watts | * RealPower in Watts | ||
* ApparentPower in Watts | * ApparentPower in Watts | ||
* Irms in Amperes | * Irms in Amperes (or Estimated Power if Vest different from 1.0) | ||
* Vrms in Volts | * Vrms in Volts | ||
* PowerFactor without units. | * PowerFactor without units. | ||
| Line 96: | Line 97: | ||
With sketch '''version 2.0 & 2.1''' and above some channels can be disabled. See this page for more info. | With sketch '''version 2.0 & 2.1''' and above some channels can be disabled. See this page for more info. | ||
[[RPICT3V1 Disable channels sketch 2]] | [[RPICT3V1 Disable channels sketch 2]] | ||
==Restore Default Config== | |||
You should have received a key when acquiring the unit. Use this key to download and restore the default configuration.<br> | |||
If the key was XXXX then execute these commands below. Replace XXXX with your own key. | |||
$ wget lechacal.com/hardware/c/XXXX.conf | |||
$ lcl-rpict-config.py -w XXXX.conf | |||
==View the data with Python== | ==View the data with Python== | ||
| Line 105: | Line 114: | ||
Then copy the following into an executable file and run it. | Then copy the following into an executable file and run it. | ||
This is below for '''sketch 2.0''' and above. | This is below for '''sketch 2.0''' and above. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | |||
#!/usr/bin/ | #!/usr/bin/python3 | ||
import serial | import serial | ||
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', 38400) | ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', 38400) | ||
| Line 148: | Line 124: | ||
while 1: | while 1: | ||
# Read one line from the serial buffer | # Read one line from the serial buffer | ||
line = ser.readline() | line = ser.readline().decode().strip() | ||
# Create an array of the data | # Create an array of the data | ||
| Line 169: | Line 142: | ||
except KeyboardInterrupt: | except KeyboardInterrupt: | ||
ser.close() | ser.close() | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
To get the above example just enter the command below. | To get the above example just enter the command below. | ||
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/example/ | wget lechacal.com/RPICT/example/RPICT3V1_DEMO.py.zip | ||
unzip | unzip RPICT3V1_DEMO.py.zip | ||
and run it using | and run it using | ||
python3 RPICT3V1_DEMO.py | |||
==Emoncms Config (Emonhub)== | ==Emoncms Config (Emonhub)== | ||
For default configuration with sketch '''version 2.0''' and above. | For default configuration with sketch '''version 2.0''' and above. | ||
| Line 223: | Line 165: | ||
==Sketch== | ==Sketch== | ||
Units are sold flashed with sketch for use with Voltage sensor. | Units are sold flashed with sketch for use with a Voltage sensor. | ||
===Usage with Voltage sensor=== | ===Usage with Voltage sensor=== | ||
[http://lechacal.com/RPICT/CT3V1/RPICT3V1_v2_0.ino Version 2.0]<br> | [http://lechacal.com/RPICT/CT3V1/RPICT3V1_v2_0.ino Version 2.0]<br> | ||
[http://lechacal.com/RPICT/CT3V1/RPICT3V1_v2.1.ino Version 2.1] → current default for sold units.<br> | [http://lechacal.com/RPICT/CT3V1/RPICT3V1_v2.1.ino Version 2.1]<br> | ||
[http://lechacal.com/RPICT/sketch/RPICT3V1_v2.2.ino Version 2.2] [http://lechacal.com/RPICT/sketch/RPICT3V1_v2.2.ino hex]→ current default for sold units.<br> | |||
===Usage without Voltage sensor=== | ===Usage without Voltage sensor=== | ||
| Line 249: | Line 188: | ||
==Related Pages== | ==Related Pages== | ||
[[Howto setup Raspbian for serial read]] | |||
[[Gen3_Passive_Component_Setup]] | |||
[[How to calibrate the Voltage Port]] | [[How to calibrate the Voltage Port]] | ||
[[How to program an Attiny85 or Attiny84]] | |||
[[Use Emonhub with RPICT]] | [[Use Emonhub with RPICT]] | ||
[[ | [[Flash RPICT Attiny84 with Arduino UNO]] | ||
==FAQ== | |||
More generic FAQ are here. | |||
[[Frequently Asked | Frequently Asked Questions]] | |||
===Why are there 3 Vrms output for only 1 Voltage port?=== | |||
The RPICT3V1 computes power using associated pairs for Current/Voltage (CV pairs). The result of this computation gives Vrms Irms ActivePower etc. | |||
The CV pairs in the RPICT3V1 are <br> | |||
P1-> CT1/V1<br> | |||
P2-> CT2/V1<br> | |||
P3-> CT3/V1<br> | |||
The output reports the result of Vrms for each of these computation. We do expect the three Vrms values to be the nearly the same with a small diffrence because there are computed at a different time. | |||
In practice for voltage monitoring you should just use one of the three Vrms. | |||
However if you need to know precisely which Vrms was used when computing a given Active Power then make sure you compare it against the Vrms it is associated with. | |||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 11 November 2023
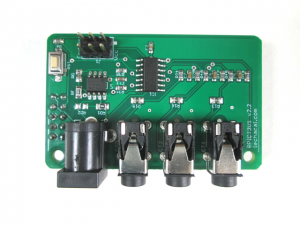
This page is for board specific information. More information can be found on the generic page for RPICT series.
- 3 AC current sensor
- 1 AC Voltage sensor.
- Compute RealPower, ApparentPower, PowerFactor, Vrms, Irms.
- Fit on the 2 holes mounting pattern for Raspberrypi.
- Arduino Attiny84 Microcontroller.
Compatibility

| Version | Compatible? |
|---|---|
| Raspberrypi 1 A | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 1 B | No mounting holes. |
| Raspberrypi 1 B+ | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 2 B | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 3 B | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 3 B+ | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 4 B | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 5 | Yes |
- Asus Tinkerboard has been reported to work with RPICT units. Note we wont be able to provide support for the Tinkerboard.
Notice
The RPICT3V1 must have a voltage sensor to compute Real Power. If you do not want to use a voltage sensor and prefer measuring just current then the RPICT3T1 might be more appropriate.
(Note it is possible to use a different sketch (firmware) to make the RPICT3V1 using estimated voltage. However you will have to flash the unit with a special programmer for that.)
Recommended sensors

- AC Current sensor:
- SCT-013-000
- SCT-019
- SCT-006
- SCT-024 400A/100mA
- SCT-031 600A/100mA
- AC Voltage sensor:
- ZMPT101B Module
- UK: 77DB-06-09
- EU: 77DE-06-09
- US: 77DA-10-09
Configuration
Starting from sketch version 1.1 the RPICT3V1 is configured over serial.
See general instructions for configuration below:
Configuration over serial for sketch version 2.0 & 2.1.
Version 2.0 & 2.1 can be configured using the web tool.
Default Data Output
If you are running an old version of the firmware click on the link below related to your version.
RPICT3V1 Sketch version 1.3 documentation
Using the default sketch version 2.0 and above the output is
NodeID Realpower1 ApparentPower1 Irms1 Vrms1 PowerFactor1 Realpower2 ApparentPower2 Irms2 Vrms2 PowerFactor2 Realpower3 ApparentPower3 Irms3 Vrms3 PowerFactor3
- RealPower in Watts
- ApparentPower in Watts
- Irms in Amperes (or Estimated Power if Vest different from 1.0)
- Vrms in Volts
- PowerFactor without units.
With sketch version 2.0 & 2.1 and above some channels can be disabled. See this page for more info. RPICT3V1 Disable channels sketch 2
Restore Default Config
You should have received a key when acquiring the unit. Use this key to download and restore the default configuration.
If the key was XXXX then execute these commands below. Replace XXXX with your own key.
$ wget lechacal.com/hardware/c/XXXX.conf $ lcl-rpict-config.py -w XXXX.conf
View the data with Python
Please note the configuration must have Emonhub format enabled (format=3). The example script below will be a good starting point.
First of all make sure you have python-serial package installed
$ sudo apt-get install python-serial
Then copy the following into an executable file and run it.
This is below for sketch 2.0 and above.
#!/usr/bin/python3
import serial
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', 38400)
try:
while 1:
# Read one line from the serial buffer
line = ser.readline().decode().strip()
# Create an array of the data
Z = line.split(' ')
# Print it nicely
if len(Z)>15:
print ("----------")
print (" \tCT1\tCT2\tCT3")
print ("RealPower:\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[1], Z[6], Z[11]))
print ("AppaPower:\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[2], Z[7], Z[12]))
print ("Irms :\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[3], Z[8], Z[13]))
print ("Vrms :\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[4], Z[9], Z[14]))
print ("PowerFact:\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[5], Z[10], Z[15]))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
ser.close()To get the above example just enter the command below.
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/example/RPICT3V1_DEMO.py.zip unzip RPICT3V1_DEMO.py.zip
and run it using
python3 RPICT3V1_DEMO.py
Emoncms Config (Emonhub)
For default configuration with sketch version 2.0 and above.
[[11]]
nodename = my_RPICT3V1
hardware = RPICT3V1
[[[rx]]]
names = RP1, AP1, Irms1, Vrms1, PF1, RP2, AP2, Irms2, Vrms2, PF2, RP3, AP3, Irms3, Vrms3, PF3
datacode = 0
scales = 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
units = W,W,A,V,.,W,W,A,V,.,W,W,A,V,.
Sketch
Units are sold flashed with sketch for use with a Voltage sensor.
Usage with Voltage sensor
Version 2.0
Version 2.1
Version 2.2 hex→ current default for sold units.
Usage without Voltage sensor
If you wish to use the board without using the voltage sensor use the sketch below. Note power will be estimated power only using fixed voltage setup in configuration.
No Voltage Version 2.0
Once the sketch uploaded write the configuration as follow:
$ wget lechacal.com/RPICT/config/A2/rpict3v1.conf $ lcl-rpict-config.py -w rpict3v1.conf
Output will be in AMps. Change VEST in config from 1 to 240 or 110 to get estimated power.
CAD Drawing
Related Pages
Howto setup Raspbian for serial read
How to calibrate the Voltage Port
How to program an Attiny85 or Attiny84
Flash RPICT Attiny84 with Arduino UNO
FAQ
More generic FAQ are here. Frequently Asked Questions
Why are there 3 Vrms output for only 1 Voltage port?
The RPICT3V1 computes power using associated pairs for Current/Voltage (CV pairs). The result of this computation gives Vrms Irms ActivePower etc.
The CV pairs in the RPICT3V1 are
P1-> CT1/V1
P2-> CT2/V1
P3-> CT3/V1
The output reports the result of Vrms for each of these computation. We do expect the three Vrms values to be the nearly the same with a small diffrence because there are computed at a different time.
In practice for voltage monitoring you should just use one of the three Vrms.
However if you need to know precisely which Vrms was used when computing a given Active Power then make sure you compare it against the Vrms it is associated with.

