RPICT7V1 v2.0: Difference between revisions
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
Then copy the following into an executable file and run it. | Then copy the following into an executable file and run it. | ||
#!/usr/bin/python2 | |||
import serial | |||
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', 38400) | |||
try: | |||
while 1: | |||
# Read one line from the serial buffer | |||
line = ser.readline() | |||
# Remove the trailing carriage return line feed | |||
line = line[:-2] | |||
# Create an array of the data | |||
Z = line.split(' ') | |||
# Print it nicely | |||
if len(Z)>15: | |||
print ("----------") | |||
print ("Vrms:\t%s" % Z[15]) | |||
print (" \tCT1\tCT2\tCT3\tCT4\tCT5\tCT6\tCT7") | |||
print ("RealPower:\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[1], Z[2], Z[3], Z[4], Z[5], Z[6],$ | |||
print ("Irms :\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[8], Z[9], Z[10], Z[11], Z[12], Z[$ | |||
except KeyboardInterrupt: | |||
ser.close() | |||
==Emoncms Config (Emonhub)== | ==Emoncms Config (Emonhub)== | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 18 March 2020
RPICT7V1 (This covers for both hardware versions 2 and 3)
This page is for board specific information. More information can be found on the generic page for RPICT series.

- 7 AC current sensors.
- 1 AC Voltage sensor.
- Measure RMS Current and Voltage, Active power, Apparent Power, Power Factor.
- Fit on Raspberrypi 4 holes mounting pattern.
- AtMega328 Mcu (Arduino UNO)
- MCP3208 ADC
- Stackable with itself, RPICT8 and RPICT4V3.
Compatibility
| Version | Compatible? |
|---|---|
| Raspberrypi 1 A | No |
| Raspberrypi 1 B+ | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 2 B | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 3 B | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 3 B+ | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 4 B | Yes |
- Asus Tinkerboard has been reported to work with RPICT units. Note we wont be able to provide support for the Tinkerboard.
Recommended sensors

- AC Current sensor:
- SCT-013-000
- SCT-019
- SCT-006
- AC Voltage sensor:
- UK: 77DB-06-09
- EU: 77DE-06-09
- US: 77DA-10-09
VOLTAGE OUTPUT CT ARE NOT COMPATIBLE WITH THIS BOARD.
Stacking Configuration
General stacking information is described in the RPICT stacking page. RPICT_Stacking
Software Configuration
Using a serial line terminal program one can configure the following:
- Polling interval - Output format (csv or emonhub) - Calibration values (Voltage and Current) - Voltage/current combinations for real power computation. - Output channels
The documentation for serial configuration can be found on this page.
Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 2.2
Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 2.3
Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 2.4
Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 2.5
Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 2.6
Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 2.8
Over Serial Configuration - Sketch 3.0
 The board can be configured with the online configurator.
The board can be configured with the online configurator.
Usage without Voltage sensor
Default configuration expect a voltage sensor to be plugged in.
The configuration rpict7v1_noV.conf will only output current Irms for the 7 channels.
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/config/B4/rpict7v1_noV.conf $ lcl-rpict-config.py -w rpict7v1_noV.conf
Files
Default Sketch
noOSC Sketch
The Default sketch allows up to 24 computation nodes to be run. If more are needed for higher stacks then we recommend to use the noOSC sketch. This is the same as the default sketch but Over Serial Configuration (OSC) as been removed to allow up to 40 nodes to be computed. Configuration has to be edited in the sketch.
noOSC Sketch v1.0
noOSC Sketch v1.1
View the data with Python
Please note the configuration must have Emonhub format enabled (format=3). The example script below will be a good starting point.
First of all make sure you have python-serial package installed
$ sudo apt-get install python-serial
Then copy the following into an executable file and run it.
#!/usr/bin/python2
import serial
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', 38400)
try:
while 1:
# Read one line from the serial buffer
line = ser.readline()
# Remove the trailing carriage return line feed
line = line[:-2]
# Create an array of the data
Z = line.split(' ')
# Print it nicely
if len(Z)>15:
print ("----------")
print ("Vrms:\t%s" % Z[15])
print (" \tCT1\tCT2\tCT3\tCT4\tCT5\tCT6\tCT7")
print ("RealPower:\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[1], Z[2], Z[3], Z[4], Z[5], Z[6],$
print ("Irms :\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[8], Z[9], Z[10], Z[11], Z[12], Z[$
except KeyboardInterrupt:
ser.close()
Emoncms Config (Emonhub)
Make sure you read this first.
For default configuration. Used as single board only (not stacked).
[[11]]
nodename = my_RPICT7V1
hardware = RPICT7V1
[[[rx]]]
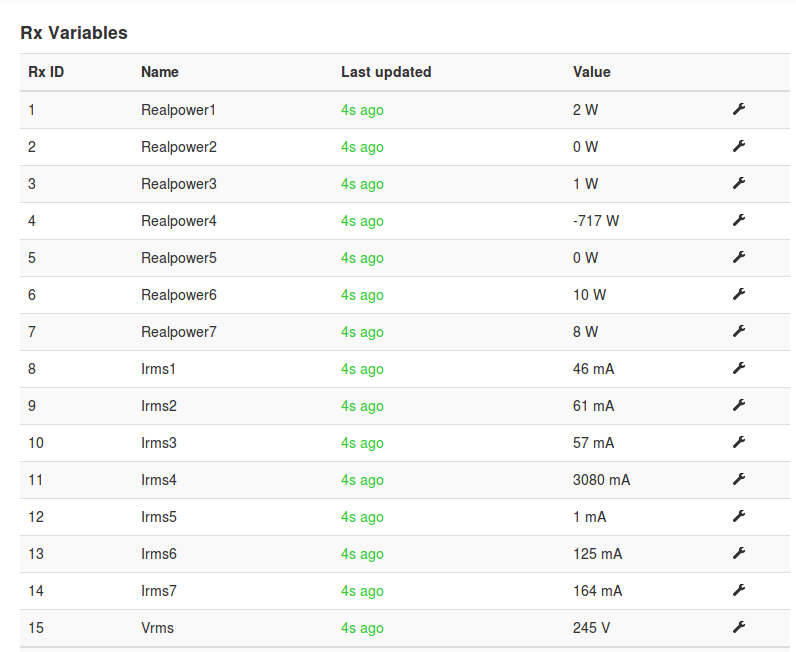
names = RP1, RP2, RP3, RP4, RP5, RP6, RP7, Irms1, Irms2, Irms3, Irms4, Irms5, Irms6, Irms7, Vrms
datacode = 0
scales = 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
units =W,W,W,W,W,W,W,mA,mA,mA,mA,mA,mA,mA,V
Related Pages
Howto setup Raspbian for serial read