Transform a RPICT into a web scope
Overview
This is to show the waveform on a web browser using the RPICT in a special configuration. We will use the Raspberrypi to collect the analog data from the RPICT and serve them as a HTTP server.
IMPORTANT. This is not a substitute for a scope. This is just a playground for demonstration.
Preliminaries
Make sure you have a fresh Raspbian image installed.
Setup the Raspbian to enable the serial port. See the guide below to complete this.
Howto setup Raspbian for serial read
Upload the Sketch
The RPICT will require a different sketch depending on the model. Download the appropriate sketch that applies.
RPICT4T4 RPICT3V1
RPICT Scope Attiny Version 1.0
RPICT3T1
coming soon.
RPICT7V1 RPICT4V3 RPICT8
Prepare the Raspberrypi for uploading new firmwares. Follow the instructions in the guide below.
Upload Arduino sketch from Raspberrypi to RPICT
Get the scope sketch.
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/sketch/RPICT_SCOPE_MCP3208_v1_4.ino.hex
Upload it to the RPICT unit.
lcl-upload-sketch.sh RPICT_SCOPE_MCP3208_v1_4.ino.hex
Read The data
On the web browser
Setup the web server
Navigate to the http public folder and install the scope webserver.
cd /var/www/html/ sudo wget lechacal.com/RPICT/scope/rpict-scope-v2.0.zip sudo unzip rpict-scope-v2.0.zip
This will create a folder called scope. There is a configuration file inside called rpict-scope.conf which should not need modification.
Now start a server instance
cd /var/www/html/ python3 -m http.server 8000
Run the service and view the data
From the raspberrypi run the command below. You might have to open a second terminal window for this.
sudo /var/www/html/scope/lcl-rpict-scope.py
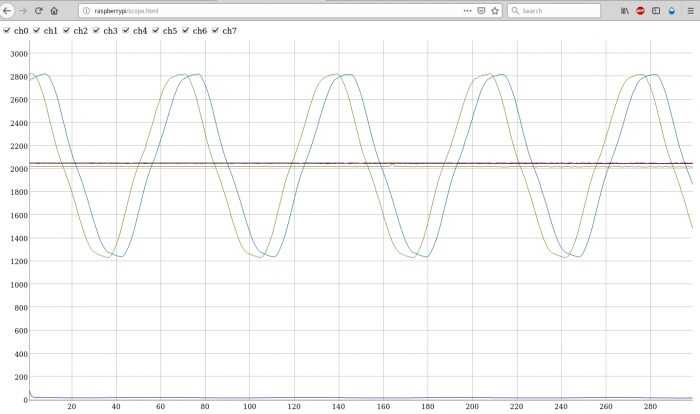
Then now open a web browser and go to address
http://raspberrypi:8000/scope/scope.html?yrange=4100
In the above address change 'raspberrypi' accordingly to your raspberrypi hostname or ip address.
Modify yrange in the address as required.
Get the data from serial port
You can read the data directly with the lcl-run command.
lcl-run
The out put format is N:d0,d1,d2,d3....dn
Where N is the channel number. d0 d1 d2 dn are the raw data points.
A simple python script to read the data would look like this below:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import serial
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', 38400)
try:
while 1:
# Read one line from the serial buffer
try:
line = ser.readline().decode().strip()
# Create an array of the data
z = line.split(':')
if len(z)>0:
channel = z[0]
data = z[1].split(',')
print(channel)
print(data)
except UnicodeDecodeError:
pass
except KeyboardInterrupt:
ser.close()
This above can be run directly with
sudo /var/www/html/scope/demo.py