RPICT4V3 Version 5: Difference between revisions
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
The documentation for serial configuration can be found on this page. <br> | The documentation for serial configuration can be found on this page. <br> | ||
[[Over_Serial_Configuration_-_Sketch_4]]<br> | |||
[[ | |||
Revision as of 16:57, 30 March 2022
RPICT4V3 Version 5

This page is for board specific information. More information can be found on the generic page for RPICT series.
Overview
- 4 AC current sensors.
- 3 AC Voltage sensors.
- Compute real power.
- Fit on Raspberrypi 4 holes mounting pattern.
- AtMega328 Mcu (Arduino UNO)
- MCP3208 12 bits ADC
- Stackable (up to 5 boards together)
A typical application for the RPICT4V3 is 3 phase systems power reading. The 3 voltages are coupled with 3 CT to perform power computation on each line.
Compatibility
| Version | Compatible? |
|---|---|
| Raspberrypi 1 A | No |
| Raspberrypi 1 B+ | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 2 B | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 3 B | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 3 B+ | Yes |
| Raspberrypi 4 B | Yes |
- Asus Tinkerboard has been reported to work with RPICT units. Note we won't be able to provide support for the Tinkerboard.
Recommended sensors
- AC Current sensor:
- SCT-013-000
- SCT-019
- SCT-006
- AC Voltage sensor:
- ZMPT101B Module
- UK: 77DB-06-09
- EU: 77DE-06-09
- US: 77DA-10-09
VOLTAGE OUTPUT CT SUCH AS SCT-013-030 and other SCT-013-0XX ARE NOT COMPATIBLE WITH THIS BOARD. Only use the SCT-013-000 which is a current output CT.
Stacking Configuration
General stacking information is described in the RPICT stacking page. RPICT_Stacking Version 5
Software Configuration
For any units ordered before the 1st of February 2022 the firmware version is version 3. Follow this link below for configuration. If possible upgrade to firmware version 4.
Before 1st March 22 RPICT4V3 Configuration
Upgrading to sketch version 4
First make sure the lcl-package is installed if not done already.
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/tools/lcl-rpict-package_v1.0.2.deb sudo dpkg -i lcl-rpict-package_v1.0.2.deb
Now starts a server instance on the Raspberrypi using.
lcl-server.sh
You can now access the Raspberrypi configuration server if you point your browser to the link below
http://raspberrypi:8000/
You can now edit the configuration.
Using a serial line terminal program one can configure the following:
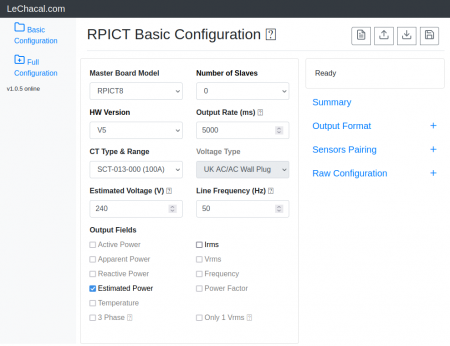
- Polling interval - Output format (csv or emoncms) - Calibration values (Voltage and Current) - Voltage/current combinations for real power computation. - Output channels
The documentation for serial configuration can be found on this page.
Over_Serial_Configuration_-_Sketch_4
Auto Reset
Version 5 units have auto reset support. When using the lcl-rpict-config.py command it is possible to reset the RPICT remotely with the -a option.
lcl-rpict-config.py -a
or
lcl-rpict-config.py -a -w myfile.conf
Files
3Phase sketch
This is the default firmware from manufacture.
This sketch can be loaded directly from the Raspberrypi following this guide and executing the commands below.
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/sketch/RPICT4V3_3Phase_V5_v1.4.ino.hex lcl-upload-sketch RPICT4V3_3Phase_V5_v1.4.ino.hex
Individual Phase Sketch
If not using the RPICT4V3 for 3 phase you can use the firmware for individual line.
This sketch can be loaded directly from the Raspberrypi following this guide and executing the commands below.
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/sketch/RPICT_MCP3208_v3.2.0.ino.hex lcl-upload-sketch RPICT_MCP3208_v3.2.0.ino.hex
Using this sketch the configuration tool below can be used to setup each channels individually.
noOSC Sketch
The Default sketch allows up to 28 computation nodes to be run. If more are needed for higher stacks then we recommend to use the noOSC sketch. This is the same as the default sketch but Over Serial Configuration (OSC) as been removed to allow up to 40 nodes to be computed. Configuration has to be edited in the sketch.
noOSC Sketch v1.0
noOSC Sketch v1.1
Simple Python Example
The example python script below will work well with the default configuration.
import serial
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyAMA0', 38400)
try:
while 1:
# Read one line from the serial buffer
line = ser.readline()
# Remove the trailing carriage return line feed
line = line[:-2]
# Create an array of the data
Z = line.split(' ')
# Print it nicely
if len(Z)>16:
print ("----------")
print (" \tCT1\tCT2\tCT3\tCT4")
print ("Vrms :\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[1], Z[2], Z[3], Z[4]))
print ("RealPower:\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[5], Z[6], Z[7], Z[8]))
print ("Irms :\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[9], Z[10], Z[11], Z[12]))
print ("P Factor :\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (Z[13], Z[14], Z[15], Z[16]))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
ser.close()To run this first of all make sure you have python-serial package installed
$ sudo apt-get install python3-serial
Then run the command below to download the script.
wget lechacal.com/RPICT/example/RPICT4V3_DEMO_02.py.zip unzip RPICT4V3_DEMO_02.py.zip
and run it using
python RPICT4V3_DEMO_02.py
Data Output
3Phase firmware
This is the default from manufacture. Using the three phase firmware the data output is:
NodeID Vrms1 Vrms2 Vrms3 Realpower1 Realpower2 Realpower3 Irms1 Irms2 Irms3 Irms4 PF1 PF2 PF3
Using this firmware channels can not be modified with the configuration. Power associations are as follow.
RealPower1 -> CT1 & V1
RealPower2 -> CT2 & V2
RealPower3 -> CT3 & V3
EstimatedPower -> CT4 & Vest
What is the difference between the 3 phase and individual phase firmware? Both can provide readings for 3 phase systems. However the 3phase firmware has been designed to compute power using v1/ct1 v2/ct2 v3/ct3 together at once. Whereas the individual phase firmware will compute them one after the other. Computing them together makes for better results in total power.
Individual Phase firmware
Using the individual phase firmware the data output is:
NodeID Vrms1 Vrms2 Vrms3 Vrms4 Realpower1 Realpower2 Realpower3 Realpower4 Irms1 Irms2 Irms3 Irms4 PF1 PF2 PF3 PF4
Real Powers are computed using the following rules:
RealPower1 -> CT1 & V1
RealPower2 -> CT2 & V2
RealPower3 -> CT3 & V3
RealPower4 -> CT4 & V3
These rules can be modified in the configuration if needed.
Other output type can be streamed out. This should be configured in the unit.
All outputs type available are
- Vrms (V)
- Irms (A)
- Real Power (W)
- Apparent Power (W)
- Power Factor
- Estimated Power
Restore Default Config
You should have received a key when acquiring the unit. Use this key to download and restore the default configuration.
If the key was XXXX then execute these commands below. Replace XXXX with your own key.
$ wget lechacal.com/hardware/c/XXXX.conf $ lcl-rpict-config.py -w XXXX.conf
Emoncms Config (Emonhub)
Make sure you read this first.
For default configuration.
[[11]]
nodename = RPICT4V3
hardware = RPICT4V3
[[[rx]]]
names = Vrms1,Vrms2,Vrms3,Vrms4,Realpower1,Realpower2,Realpower3,Realpower4,Irms1,Irms2,Irms3,Irms4,PF1,PF2,PF3,PF4
datacode = 0
scales = 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
units = V,V,V,V,W,W,W,W,mA,mA,mA,mA
Enclosure
Enclosures kit are available as a 3D printed product. Link to the shop.
Both Raspberrypi 3 and 4 format are available.
Related Pages
Howto_setup_Raspbian_for_serial_read
How to calibrate the Voltage Port